A conventional, controlled, technical or linear approach is now not able to grapple with the newly complex and sensitive needs of modern society. Design thinking works best wherein we want to make human feel of things, drawing near challenges in ways that best fit human desires regardless of the scale or authority of the challenge.
| “ We can’t solve problems by using the same kind of thinking we used when we created them”
– Albert Einstein |
What is Design Thinking?
Design Thinking is a problem-solving framework that provides a solution-based approach to solving problems. It’s extremely useful in tackling complex problems that are ill-defined or unknown, by understanding the human needs involved, and by re-framing the problem in human-centric ways. The concept has been around for decades, but in the past, five to ten years, IDEO an international design and consulting firm and Stanford, have championed the process as an alternative to a purely analytical approach to problem-solving. Design Thinking will enable anyone to apply the Design Thinking methods in order to solve complex or wicked problems that occur around us — in our companies, societies, countries, and even our planet.
Design Thinking employs divergent thinking as a manner to confirm that many conceivable solutions are explored, and then convergent thinking as a manner to narrow these down to a final preferred solution. Divergent thinking is the potential to offer extraordinary, unique or variant notions adherent to one theme while convergent thinking is the ability to find the preferred solution to the given problem.
| “Design Thinking is a human-centered design approach to innovation that draws from the designer’s toolkit to integrate the needs of people, the possibilities of technology and the requirements for business success”
-Tim Brown |
Why Design Thinking is better than the traditional approach?
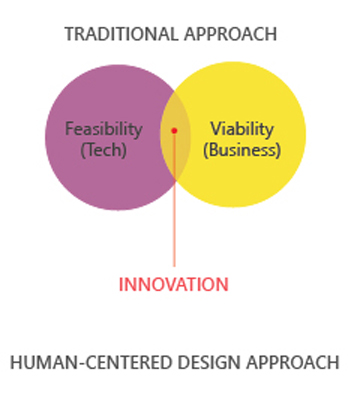
Traditional business solution approach focused only on two main aspects
1) Feasibility (technical): -A feasible solution, building on the strengths of your current operational capabilities.
2) Viability (business): -A profitable solution, with a sustainable business model.
These two metrics solve the problem in a very reasonable way. Moreover, this approach fails to uncover the user’s unmet needs, problems, and insights.
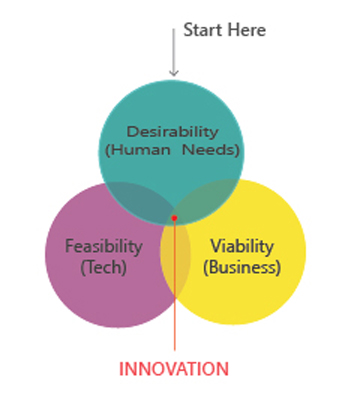
Design Thinking, on the other hand, is a human-centered design approach that starts with understanding the needs of the humans (desirability) and bringing the viability and feasibility aspects together.
1) Desirability (humans): -A desirable solution, one that your customer really needs
2) Feasibility(technical): -A feasible solution, building on the strengths of current operational capabilities.
3) Viability (business): -A profitable solution, with a sustainable business model.
Design thinking incorporates analytical, synthetic, divergent and convergent thinking to create a wide number of potential solutions.
The power of Design Thinking
Design Thinking method provides a way to discover user needs that users themselves might not be aware of. It then connects the exploration to a creative, collaborative process that ends in tangible prototypes that can be tested and verified. The development method doesn’t end there, clearly, and there are numerous potential difficulties and challenges along the way. Design Thinking can ensure that you don’t start your innovative work heading off in the wrong direction.
| “The mission of design thinking is to translate observation into insights and insights into products and services that will improve lives.”
– Tim Brown
|
Design Thinking Process

2. DEFINE: Defining the problem in human-centric ways.
3. IDEATE: Generating numerous ideas in ideation sessions.
4. PROTOTYPE: Adopting a real-world approach in prototyping.
5. TEST: Obtaining a solution to the problem.

Empathize
The first phase of the Design Thinking process is to gain an empathic understanding of the problem you are trying to solve. This involves consulting experts finding out more about the area of concern through looking at and empathizing with humans to recognize their studies and motivations, as well as immersing yourself within the physical environment to have a deeper personal understanding of the problems involved.
Why Empathize?
As a human-centered designer, you need to understand the humans for whom you’re designing. The issues you are attempting to resolve are rarely your own—they are those of users. So as to design for your users, you must build empathy for who they’re and what’s essential for them.
Observing what humans do and how they interact with their surroundings gives you clues about what they think and experience. It lets you study what they want. By observing humans, you can seize the bodily manifestations of their experiences, what they do and say. This will allow you to interpret the impalpable meaning of those experiences to reveal insights. These insights will lead you to innovative solutions.
| “The mission of design thinking is to translate observation into insights and insights into products and services that will improve lives.”
– Tim Brown
|
| “Empathy is seeing with the eyes of another, listening with the ears of another and feeling with the heart of another.”
– Alfred Adler
|

Define
The define phase is when you are taking out and creating your empathy findings into convincing desires and insights and scope a specific and meaningful challenge. it is a mode of “focusing” instead of “flaring” in a human-centered way
During the define phase, you put together the facts you have created and accumulated during the Empathize stage. you will analyze your observations and synthesis them to define the main issues which you and your team have identified so far. You should try to describe the problem as a problem statement in a human-centered manner.
Why Define?
The define phase is crucial to the design process since it clearly expresses the problem you are striving to address through your efforts. Often, to be truly generative, you must first reevaluate the challenge based on new insights you have gained through your design work. This reevaluated problem statement further can be used as a solution-generating springboard.
| “If I had an hour to solve a problem I’d spend 55 minutes thinking about the problem and 5 minutes thinking about solutions.”
– Albert Einstein
|

Ideate
During the third phase of the Design Thinking process, start producing radical design notions. It denotes a process of “going wide” regarding ideas and outcomes—it is a mode of “flaring” rather than “focusing.” The goal of ideation is to discover an extensive solution space both huge quantity of ideas and variety among these ideas. From this enormous depository of ideas you can build prototypes to test with users.
Why Ideate?
You ideate so that you can transition from identifying problems into disc¬overing solutions for your users. Diverse forms of ideation are leveraged to:
• Step beyond obvious solutions and thus increase the innovation potential of your solution set
• Harness the collective perspectives and strengths of your teams
• Uncover unexpected areas of exploration
• Create fluency (volume) and flexibility (variety) in your innovation options
• Get obvious solutions out of your heads, and drive your team beyond them
Irrespective of what idea generation technique you use, the fundamental principle of idea generation is to be cognizant of when you and your team are producing ideas and when you are assessing ideas—typically keeping these two tasks separate, and only mixing the two intentionally.
| “Ideas shape the course of history”
-John Maynard Keynes
|
| “The best way to have a good idea is to have lots of lots of ideas” -Linus Pauling
|

Prototype
Prototyping is getting notions and explorations out of your head and into the physical world. A prototype can be anything that takes a physical form be it a wall of post-it notes, a role-playing activity, a space, an object, an interface, or even a storyboard. The resolution of your prototype needs to be proportionate with your progress in your project. In early explorations keep your prototypes rough and rapid to allow yourself to learn quickly and investigate a lot of different options.
Prototypes are the most successful when people (the design team, user, and others) can experience and interact with them. What you learn from those interactions can help drive deeper empathy, as well as shape successful solutions.
Why Prototype?
Conventionally prototyping is thought of as a way to test functionality. However, prototyping is used for various reasons, including these categories:
• Empathy gaining: Prototyping is a tool to deepen your understanding of the design space and your user, even at a pre-solution phase of your project.
• Exploration: Build to think. Develop multiple solution options.
• Testing: prototypes allow to test and refine solutions with end-users.
• Inspiration: Inspire others (teammates, clients, customers, and investors) by showing your vision.
| “Prototyping is the conversation you have with your ideas”
-Tom Wujec
|
| “I love taking an idea to a prototype and then to a product that millions of people use”
– Susan Wojcicki
|

Test
Testing is one of the ways to get feedback on your solutions, improve solutions to make them better, and continue to study about your users. The test method is an iterative method where you place your low-resolution artifacts in the suitable context of the user’s life.
“This is the final phase of the 5-phase–model. However, in an iterative process, the results produced through the testing phase are frequently used to redefine one or more problems and inform the understanding of the users, the conditions of use, the way people think, behave, and feel, and to empathize. Even during this phase, alterations and enhancements are made in order to eliminate problem solutions and derive a deep understanding of the product and its users as much as possible.”
.
Why Testing?
To improve your prototypes and solutions. Testing informs the following iterations of prototypes. Sometimes this indicates going back to the sketch board.
To study more about your user. Trying out is another possibility to build empathy through observation and engagement—it regularly yields sudden insights.
To test and improve your point of view (POV). Testing not only reveals that you got the wrong solution, but also that you have failed to frame the problem properly.
| “Always prototype as if you know you’re right, but test as if you know you’re wrong — testing is the chance to refine your solutions and make them better.”
-Waag society for art
|
| “Your most unhappy customers are your greatest source of learning”
-Bill Gates
|
Design Thinking Success Story
Airbnb – How design thinking transformed Airbnb from a failing startup to a billion-dollar business. The company has gone from making 200 euros a week to revolutionizing tourism.

“We noticed a pattern. There’s some similarity between all these 40 listings. The similarity is that the photos sucked. The photos were not great photos. People were using their camera phones or using their images from classified sites. It actually wasn’t a surprise that people weren’t booking rooms because you couldn’t even really see what it is that you were paying for.”
According to Gebbia, previous to this revelation, the founders had focused on technical solutions for any problem. They were sure that better coding could improve the website and bring in more business. But suddenly they realized that the problem was not technical and could not be fixed with better programming. Instead, they decided to visit the properties in New York City which were listed on the site and replace the low-quality photographs with professional pictures. In just a week, revenue doubled, and the company realized it was OK to do things that weren’t scalable.
Gebbia realized that Airbnb would only succeed if employees went out to meet customers in the real world and worked to solve their problems. He recalled an experience he had had in design thinking, where the designers of a medical device actually lay in a bed and had the device applied to them. This experience led the designers to understand what it felt like to be a patient and what was uncomfortable about the device. Gebbia incorporated this technique into Airbnb’s culture. Every new employee is sent on a trip to one of the properties listed on the website and documents the experience. He or she answers structured questions and shares the answers with the entire company. In addition to the helpful feedback the employee provides, the trip also makes it clear to each new recruit how important the customer experience is to the company.
Airbnb has gone from making 200 euros a week to revolutionizing tourism: more than 4 million listings in 191 countries,151 million users and 65,000 cities with a total number of roomers more than 40 million in 2017. Design thinking turned the company around and made it into the success it is today.
https://blog.triode.ca/2015/03/09/how-design-thinking-saved-airbnb-from-failure/
These companies achieved business growth by focusing on Design Thinking
1. Path ($66.15M investment)
2. Two Leaves and a Bud (34% increase in revenue)
3. Wacom (300% increase in traffic)
4. Netflix (user engagement)
5. FirstSTREET (400% increase in sales)
6. Nickelodeon (#1 app for kids in app store)
7. Airbnb ($24B valuation)
8. Optimizely (46.3% more accounts)
9. Harry’s ( $136.5M investment)
Conclusion
In today’s emerging digital world, organizations face numerous challenges. These include disruptive technologies, economic and political pressures, as well as keeping up with changes in customer behavior.
To build a truly innovative and useful product, you don’t need to start with the brightest idea or the fanciest technology. You just need to start by understanding people.
References
1) https://blog.triode.ca/2015/03/09/how-design-thinking-saved-airbnb-from-failure/
2) https://www.interaction-design.org/
About The Author

As an experienced Design Thinking Evangelist, UX Strategist, Digital Experience Leader & Product Designer who has maximum user empathy. He designed innovative products for both consumers and enterprise solution users and deployed across multiple industries, technologies, and devices. HCI, HCD, UX, Cognitive Psychology and Design Thinking are areas of interest.

